
Michigan Medicine asks, What is the Most Important Occupation of Your Life? University of Michigan must gather occupational data following the Standards prescribed by Clinical Medicine

Excerpt: The Michigan Medicine AHEAD study is examining the efficacy of a medication aimed at preventing Alzheimer’s Disease in individuals at increased risk of developing the disease. The study has, however, faced criticism regarding its focus on years of schooling and its lack of a research protocol to verify the identity and individuality of the human organism. Critics assert that biological processes like the flow of biological information and protein synthesis are not influenced by education level and that individuality should not be tied to factors such as race and ethnicity. The conceptualization of “life as knowledge in action” and that it is an interplay of cellular function and knowledge must be explored.

The AHEAD Study is researching the safety and effectiveness of an investigational medication in people who might be at increased risk for developing memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. The study is looking for participants age 55-80 years old, who have generally normal memory function in daily life, and who are not being treated for memory problems. For individuals age 55-64 years old, an additional risk factor is required, such as a parent or sibling with Alzheimer’s Disease or previous biomarker testing showing increased risk for developing Alzheimer’s Disease. This study sees participants in Ann Arbor. Contact Lauren Mackenzie at spearsl@med.umich.edu or 734-232-2415.

On Tuesday, December 05, 2023, at the Michigan Clinical Research Unit (MCRU) at the Cardiovascular Center (CVC), I was interviewed for participating in the AHEAD Study and I completed the Stage 1A of the Screening process. I am asked to provide information about the most important occupation of my life, my sexual orientation, my race and ethnicity in the context of my place of birth and the country of origin, the total number of years I spent in the School to register my personal identity for participation in the Medical Research Project. The Research Protocol has not identified the basis for discovering the identity of a multicellular human organism. I can answer the questions I am asked. Do I have the ability to communicate my answers to the cells of my own body and reflect that identity in the living functions they perform to keep me alive?
The Rudi Connection at Whole Foods discards the fundamentally flawed Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) for its False Assumptions

Yes indeed, Life is Complicated. The Complexities of Life involve the man-made or human laws that control, regulate, govern, and operate the man’s Work Life without any concern for the scientific basis for the man’s existence in the natural world.

The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) is flawed as all of its assumptions about Life and Living Things are false.

All living things are complex. All living things are intelligent. All living things process and use very complex information to perform the basic living functions such as the Metabolism to survive in nature.

The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) was signed into law on June 25, 1938 claiming that it will provide protection to people working in the US.

In my analysis, FLSA is fundamentally flawed for it divides workers into categories such as “White Collar” and “Blue Collar” without understanding the basis for the man’s existence in the natural world.

There can be no distinction such as the Skilled and Unskilled among the workers as Life can only be defined as ‘Knowledge in Action’. All human beings process similar kind of information and use chemical energy to perform similar kinds of sequential, guided, purposeful and goal-oriented actions described as ‘Metabolism’. In fact, no man can perform Unskilled work.

I ask the US Congress and The US Department of Labor to discard the flawed Act and dump it into the dustbin to put an end to the division of workers into White and Blue Collar. As such, each employee and his or her employer must make the determination about compensation or remuneration and agree upon the terms for wages and benefits for performing any kind of labor.


In my view, the Natural Sciences and the Medical Science in particular does not validate the concept of the White-Collar or the Managerial Class as no human being performs executive, administrative, or professional service while operating the metabolic functions of human bodies of their own. No man lives as the boss, the manager, the administrator, the executive officer, the ruler, the governor, or the controller of his own body.

I ask my readers to reject the assumptions and the criteria described by the Fair Labor Standards Act as they contribute to Unequal Employment Opportunities at the American Workplace. As such the Fair Labor Standards Act is not consistent with the Natural Law principle of Equality that formulates the Supreme Law of this Land.

FACT SHEET – WAGE AND HOUR DIVISION (WHD) – U.S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR

Clipped from: https://www.dol.gov/whd/overtime/whdfs17s.htm
Fact Sheet #17S: Higher Education Institutions and Overtime Pay Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
The FLSA requires that a non-exempt employee receive minimum wages for his or her work, as well as overtime wages whenever he or she works more than 40 hours in a workweek. Section 13(a)(1) of the FLSA, however, exempts certain employees who perform bona fide executive, administrative, professional, and outside sales duties from minimum wage and overtime requirements. These exemptions are often called the “white-collar” exemptions. This fact sheet discusses the applicability of these exemptions to jobs that are common in higher education institutions.
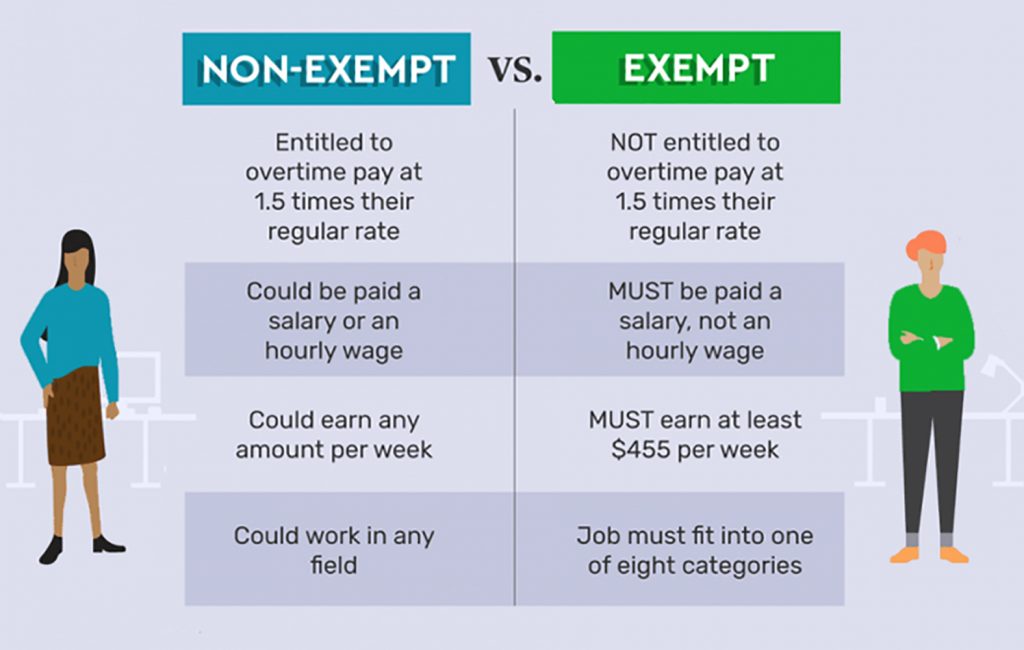
General Requirements for Exemptions
To qualify for a white collar exemption, an employee must generally satisfy three tests:
1. The employee must be paid on a salary basis that is not subject to reduction based on the quality or quantity of work (the “salary basis test”), rather than, for example, on an hourly basis;
2. The employee must receive a salary at a rate not less than $455* per week (the “salary level test”); and
3. The employee’s primary duty must involve the kind of work associated with the exempt status sought, such as executive, administrative, or professional work (the “duties test”).
4. Additional information concerning these exemptions is available in Fact Sheets 17A-G. See https://www.dol.gov/whd/regs/compliance/whdcomp.htm.
Exemptions for Common Higher Education Jobs
Teachers
A teacher is exempt if his or her primary duty is teaching, tutoring, instructing, or lecturing to impart knowledge, and if he or she is performing that duty as an employee of an educational establishment. See 29 C.F.R. § 541.303. Educational establishments include elementary school systems, secondary school systems, institutions of higher education, and other educational institutions. See 29 C.F.R. § 541.204(b). If a bona fide teacher meets this duty requirement, the salary level and salary basis tests do not apply. See 29 C.F.R. §§ 541.303(d), 541.600(e). Given these standards, professors, instructors, and adjunct professors typically qualify for this exemption.
A faculty member who teaches online or remotely also may qualify for this exemption. The regulations do not restrict where bona fide teaching may take place, to whom the knowledge can be imparted, or how many hours a teacher must work per week to qualify for the exemption. The exemption would therefore ordinarily apply, for example, to a part-time faculty member of an educational establishment whose primary duty is to provide instruction through online courses to remote non-credit learners. The exemption could likewise apply, for example, to an agricultural extension agent who is employed by an educational establishment to travel and provide instruction to farmers, if the agent’s primary duty is teaching, instructing, or lecturing to impart knowledge. To determine a teacher’s primary duty, the relevant inquiry in all cases is the teacher’s actual job duties. Job titles or full/part-time status alone do not determine exempt status.
A teacher does not become non-exempt merely because he or she spends a considerable amount of time in extracurricular activities (such as coaching athletic teams or supervising student clubs), provided the teacher’s primary duty is teaching.
Coaches
Athletic coaches employed by higher education institutions may qualify for the teacher exemption. After all, teaching may include instructing student-athletes in how to perform their sport. But a coach will not qualify for the exemption if his or her primary duties are recruiting students to play sports or visiting high schools and athletic camps to conduct student interviews. The amount of time the coach spends instructing student-athletes in a team sport is relevant, but not the exclusive factor, in determining the coach’s exempt status.
Professional Employees
The FLSA provides for several kinds of exempt professional employees—such as learned professionals, creative professionals, teachers, and employees practicing law or medicine. In higher education, employees eligible for the professional exemption are often either teachers (as discussed above) or learned professionals (as described below). To qualify as a learned professional, the employee must satisfy three requirements:
1. The employee’s primary duty must be the performance of work requiring advanced knowledge;
2. The advanced knowledge must be in a field of science or learning; and
3. The advanced knowledge must be customarily acquired by a prolonged course of specialized intellectual instruction.
See 29 C.F.R. § 541.301. Unless the employee is a teacher or practicing law or medicine, he or she must also satisfy the above-referenced salary basis and salary level tests to be an exempt professional.
In higher education, examples of exempt non-teacher learned professionals generally include certified public accountants, psychologists, certified athletic trainers, and librarians. Postdoctoral fellows, who conduct research at a higher education institution after completing their doctoral studies, likewise generally meet the duties requirements of the learned professional exemption, and they may additionally qualify for the teacher exemption if teaching is their primary duty. Of course, an employee’s qualification for the exemption depends on his or her actual job duties and education. Job titles alone are not sufficient for determining whether an employee satisfies the duties test.
Administrative Employees
Various employees at higher educational institutions may qualify as exempt administrative employees. The administrative exemption applies when the following requirements are met:
1. The employee’s compensation must satisfy the above-referenced salary basis and salary level tests;
2. The employee’s primary duty must be the performance of office or non-manual work directly related to the management or general business operations of the employer or the employer’s customers; and
3. The employee’s primary duty must include the exercise of discretion and independent judgment with respect to matters of significance.
See 29 C.F.R. § 541.200. Such administrative employees in higher education might include, for example, admissions counselors or student financial aid officers. An employee’s qualification for the exemption depends on his or her actual job duties; job titles alone are not sufficient for determining whether an employee satisfies the duties test.
Notably, there are specific regulatory provisions for certain administrative employees—known as “academic administrative employees”—whose primary duty is performing administrative functions directly related to academic instruction or training in an educational establishment. To be exempt as an academic administrative professional:
1. The employee must satisfy the above-referenced salary basis and salary level tests or receive a salary of at least the entrance salary for teachers in the same educational establishment; and
2. The employee’s primary duty must be to perform administrative functions directly related to academic instruction or training in an educational establishment.
See 29 C.F.R. § 541.204. Employees who work in higher education but whose work does not relate to the educational field (such as work in general business operations) do not qualify as exempt academic administrative employees. See id.
In higher education institutions, exempt academic administrative personnel generally include department heads, intervention specialists who are available to respond to student academic issues, and other employees with similar responsibilities. Exempt administrative personnel would likewise generally include academic counselors who administer school testing programs, assist students with academic problems, and advise students concerning degree requirements. Again, whether an employee satisfies the duties test for these exemptions depends on the employee’s actual job duties, not just the employee’s job title.
Executive Employees
To qualify for the executive exemption, an employee must satisfy the following tests:
1. The employee must receive compensation that satisfies the above-referenced salary basis and salary level tests;
2. The employee’s primary duty must be managing the enterprise or a customarily recognized department or subdivision thereof;
3. The employee must customarily and regularly direct the work of at least two or more other full-time employees or their equivalent (for example, one full-time and two half-time employees); and
4. The employee must have the authority to hire or fire other employees, or in the alternative, the employee’s suggestions and recommendations as to the hiring, firing, advancement, promotion, or any other change of status of other employees must be given particular weight.
See 29 C.F.R. § 541.100. Various positions in higher education institutions might qualify for the executive exemption, including deans, department heads, directors, and any other manager or supervisor whose job duties and compensation satisfy the above criteria.
Student-Employees
As a general matter, most students who work for their college or university are hourly non-exempt workers and do not work more than 40 hours per week. The following, however, are examples of students who often receive a salary or other non-hourly compensation:
· Graduate Teaching Assistants. Graduate teaching assistants whose primary duty is teaching are exempt. Because they qualify for the teacher exemption, they are not subject to the salary basis and salary level tests.
· Research Assistants. Generally, an educational relationship exists when a graduate or undergraduate student performs research under a faculty member’s supervision while obtaining a degree. Under these circumstances, the Department would not assert that an employment relationship exists with either the school or any grantor funding the student’s research. This is true even though the student may receive a stipend for performing the research.
· Student Residential Assistants. Students enrolled in bona fide educational programs who are residential assistants and receive reduced room or board charges or tuition credits are not generally considered employees under the FLSA. They therefore are not entitled to minimum wages and overtime under the FLSA.
An employment relationship will generally exist when a student receives compensation and his or her duties are not part of an overall education program. For example, students who work at food service counters, sell programs or usher at events, or wash dishes in dining halls and anticipate some compensation (for example, money or meals) are generally considered employees entitled to minimum wage and overtime compensation.
Compensatory Time at Public Universities
Public universities or colleges that qualify as a “public agency” under the FLSA may compensate non-exempt employees with compensatory time off (or “comp time”) in lieu of overtime pay. A college or university is a public agency under the FLSA if it is a political subdivision of a State. When determining whether a college or university is a “political subdivision,” the Department considers whether (1) the State directly created the entity, or (2) individuals administering the entity are responsible to public officials or the general electorate.
If the public university or college qualifies as a public agency, non-exempt employees generally may not accrue more than 240 hours of comp time. However, employees engaged to work in a public safety activity, an emergency response activity, or a seasonal activity may accrue as much as 480 hours of comp time. See 29 U.S.C. 207(o)(3)(A). Private higher education institutions may not pay employees comp time in lieu of overtime pay.
Where to Obtain Additional Information
This publication is for general information and is not a regulation. For additional information, visit our Wage and Hour Division Website: http://www.wagehour.dol.gov and/or call our toll-free information and helpline, available 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. in your time zone at: 1-866-4USWAGE (1-866-487-9243).
The Department of Labor is undertaking rulemaking to revise the regulations located at 29 C.F.R. part 541, which govern the exemption of executive, administrative, and professional employees from the Fair Labor Standards Act’s minimum wage and overtime pay requirements. Until the Department issues its final rule, it will enforce the part 541 regulations in effect on November 30, 2016, including the $455 per week standard salary level. These regulations are available at: https://www.dol.gov/whd/overtime/regulations.pdf.



The Rudi Connection at Whole Foods describes Intelligence as a Spiritual Function

Yes indeed, Life is complicated. To know about the complexities of Life, the man requires a theory of Knowledge. How does the multicellular organism called man knows the fact of its own existence? How does the multicellular organism knows the Identity of the singularity called man who exists in the world reaping the benefits of life supporting living functions performed by the independent, individual building blocks of his body? The Rudolf-Rudi Connection at Whole Foods describes The Cognitive Theory of Human Existence.
SPIRITUALISM AND INTELLIGENCE:

What is Man? I would begin this investigation by sharing my motivation for asking this question. The motivation comes from a statement that is expressed in Sanskrit language: “SARVESHAM SVASTIR BHAVATU”, a statement that seeks the well-being of all people, of all races, of all cultures, of all religions, and of all nations.

The meaning and purpose of life are affected by whatever we think is the real or true nature of man. It is important to recognize that our efforts to support the well-being of man would require correct understanding and knowledge of the real or true man.
WHAT IS INTELLIGENCE?

Intelligence can only exist in living matter and living entities. The word Intelligence (Latin. Intelligentia) involves perception, discernment, the ability to learn or understand from experience, and the ability to acquire and retain knowledge. Intelligence is associated with all-around effectiveness of a living organism to maintain its existence. Intelligence influences a broad range of living functions and could be observed in the performance of those functions.
The potentiality or capacity called Intelligence has a biological basis. However, in popular usage, Intelligence is used to describe the cognitive (knowing) component distinct from the affective (emotional), and motivational (drive) components of human behavior. Very often, people use the term Intelligence to describe the variations in the ability to learn, to function in society and to behave according to contemporary social expectations. I would like to differ from this conception of Intelligence as an innate ‘brain- power’- a mental faculty which distinguishes the more highly evolved animals from simple organisms, and tries to measure Intelligence levels and the differences among individuals and separate geniuses from average persons.
It is not reasonable to think of Intelligence as an exclusive function or faculty of the mind. Psychologists who describe the psychological basis of Intelligence tend to view Intelligence as a combination of the innate characteristics of an individual’s Central Nervous System which is molded by experience, learning, heredity, and environmental factors. Psychologists describe Intelligence as a collection of a large number of highly varied, although overlapping mental skills and abilities. Intelligence may include about 120 specific abilities which are grouped under three categories as: 1. logical processes, 2. the kinds of information processed, and 3. the products of such information processed (eg. classes, systems, relations).
It is understandable to know Intelligence as multidimensional and Intelligence serves as the basis for the performance of a wide variety of functions that involve knowing information, use or application of information, and physical performance or observed behavior which could be called Intelligent Behavior. Still, there is no single definition of Intelligence. There is no agreement if Intelligence could be directly observed and be accurately measured. Intelligence remains as a hypothetical ability. There is an abstract faculty that apprehends, conceptually and perceptually, relations among objects.
I present this abstract function of Intelligence to recognize relations among objects as a feature of a living cell and its ability to recognize the presence of other living cells present in its environment, its ability to recognize substances present in its environment, its ability to selectively use or dispose of molecules, its ability to express cooperation, tolerance, mutual assistance, defence, communication, and functional subordination in various biotic interactions with its own being, or in its interactions with other living species.
My purpose is that of recognizing the fact of Intelligence as the characteristic of all living organisms and living cells and it could be important to recognize the association between Intelligence and Consciousness as the basis for a living entity to exist in its environment. We cannot afford to ignore the fact that millions of human beings have perished because of Intelligence displayed in operation and behavior of a variety of Viruses, Bacteria, Protozoa, and other parasites.
SPIRITUALISM AND INTELLIGENCE:


We must make a distinction between Intelligence and Intellect, the mental function which is associated with Thinking. Brain like all other organs and tissues of the human body grows and develops from the protoplasm of a single, fertilized egg cell. The intellectual abilities of brain are dependent upon the basic, underlying nature and ability of its living matter or protoplasm. Intelligence represents innate ability or capacity to learn and adapt. It describes the ability to acquire new knowledge from experience. This potentiality and capacity of Intelligence is reflected in mental abilities like creative thinking and analytical thinking.
In my view, both Consciousness, and Intelligence are the defining features of Soul or Spirit. For that reason, I submit that the living matter or protoplasm is of Spiritual nature as it knows to formulate its relations with other living entities with a nature that exhibits traits of Compassion, Sympathy, and Understanding to achieve both internal, and external Harmony, Tranquility, and Peace to support its existence and living condition. Man because of his intellectual abilities entertains thoughts about immortality, eternal life, and everlasting life as he recognizes the potentiality and capacity of his Intelligence that sustains and maintains his living condition.
Simon Cyrene
The Rudolf-Rudi Connection proposes a Cognitive Theory of Human Existence

Spiritualism – The Cognitive Science of Spirituality:
The term cognition is derived from Latin word cognitio which means knowledge which is related to the Latin word cognoscere ( co-, together + gnoscere, know) which means the act or process of knowing. Cognitive Science involves the study of all human activities related to knowledge. These activities include attention, creativity, memory, perception, problem solving, thinking, and the use of language.

Cognition is the process involved in knowing, or the act of knowing which includes awareness and judgment. Cognition is often viewed as a psychological function and its nature is described as the relationship between the knowing mind and external reality.

The Cognitive Science of Spirituality that I would like to describe is related to the cognitive abilities of a living cell or living organism; the abilities such as recognition, responsiveness, communication using signals, memory, ability to process, store, retrieve, and use information that could be innate or acquired, the ability of adaptation to changing internal or external environmental conditions, and the fact of awareness of its own existence; the awareness of its internal condition, and the awareness of its external environment.

The purpose of the Cognitive Science of Spirituality is not that of describing a cognitive theory of human personality. The Behavioral Science is primarily involved in the study of stimuli and responses; it observes human activities particularly social behavior and not that of higher mental processes which are not available to direct examination. While Cognitive Science is concerned with mind’s ability to acquire, process, store, and use information, the information processed need not be represented in cortical awareness. Cognitive Psychology does not rely on conscious introspection or mental reflection.

The Cognitive Science of Spirituality that I describe does not involve acts of Meditation or mental introspection to discover the spiritual nature of man. I suggest that Spiritualism can be understood without regard to the machinery of brain/mind’s information processing. The organism that we all know as Amoeba (Greek word – ‘Amoibe’ which means change) is a spiritual entity as it is Conscious or Aware of its existence, it shows responsiveness by changing its shape as it likes, it is Intelligent for it uses, processes, stores, retrieves, and uses information to perform its metabolic functions, and it displays abilities such as adaptation and memory of its acquired experience. I tend to view these biological functions and characteristics as an attribute of the spiritual nature of its living substance and this spiritual nature brings functional harmony to sustain its existence as a biological entity.
The Theory of Knowledge and the Cognitive Science of Spiritualism:

I am not concerned about Bertrand Russell’s skeptical atheist temperament. The Spiritualism that I describe is not about religious faith or belief and the Spirituality that I write about is not concerned with religious practices or rituals. I claim that man is a Spiritual being because of the spiritual nature of his living matter or living substance. It is important to know that Russell was determined not to be beguiled by human pretensions to knowledge. He had never supported unbacked assumptions either about the foundations of knowledge or about what may be said to exist. He endorsed the application of rationality to all aspects of human thought and language. He was seriously concerned with the application of logical analysis to epistemological questions and attacked this problem by trying to breakdown human knowledge into minimum statements that were verifiable by empirical observation, reason, and logic. He was convinced that all knowledge is dependent on sense experience. His primary aim was to inquire with skeptical intent, “how much we can be said to know and with what degree of certainty or doubtfulness.” In 1898, with Trinity Fellow G.E. Moore, he rebelled against Idealism and became an Empiricist, a Positivist, and a Physical Realist or a Materialist. He held that the scientific view of the world is largely the correct view. He addressed the problem of the pretensions of human knowledge in his books, An Inquiry into Meaning and Truth (1940) and Human Knowledge, Its Scope and Limits (1948). His aim was also analytic and he assumed that it is possible to infer something about the world from the language in which it is correctly described. Russell analyzed that language must be used to state its minimum requirements, its atomic facts and avoid the use of descriptive phrases which may postulate the existence of objects. He held that a proposition is a picture of the facts that it asserts and must have in a sense the same structure. He stressed the importance of similarity of structure as a criterion in inferring causal relationships.

In a Lecture titled ‘Why I am not a Christian’ given on March 06, 1927, Russell explained the nature of his beliefs about God and Mortality. In his opinion and personal belief, he held the view that Life suitable to Protoplasm could be possible under certain physical conditions like temperature. Russell’s speculative assumption about the existence of Life or Protoplasm is not supported by scientific evidence. He had no scientific data to support his view. The ideal conditions for Life and Protoplasm exist right now and what we know is that Life is always born from previously existing Life. However, he had concluded his Lecture by stating that, “it needs hope for the future……., the future that our intelligence can create.”

Russell’s assumption that human intelligence is the basis for man’s biological existence is incorrect and is not consistent with the scientific reality about human existence and its nature. At a very fundamental level, man’s ability to acquire energy from an external source in the physical environment does not depend upon his physical or mental work or effort. If green plants with Chloroplasts have the ability to trap Sun’s energy, it could not be attributed to man’s intelligence. The fact of Chloroplasts and their ability is not dependent on man having any kind of intelligence. Russell’s theoretical claims have no relationship with observational evidence and his opinions could be easily refuted for lack of validity. Physical Sciences and Biological Sciences provide accepted body of information about the world and human body. We need to arrange this information into a meaningful pattern and interpret it to describe the reality.
The purpose of the Cognitive Science of Spiritualism is to describe and codify observations and experiences to explain the biological basis for human organism in its given environment as an individual, and as a member of a biological community.

