The Spiritual Beginning of Life on Earth

I use the term ‘Spiritual’ to describe relationships between entities based upon shared values, feelings, thoughts, interests, and purposes. A Living Cell is the Building Block of Life. Its primary purpose in Life is Generation and Propagation of entities of its own kind to sustain its existence. To perform such living functions, Cell requires energy input from its external environment. The Spiritual Dimension of Living Cell involves its ability to acquire energy from an external source. In Physiology, the term Nutrition describes the Power of Living Cell to attract matter (or energy yielding molecules) from its external environment. The issue that concerns me is that of the Origin or Beginning of this Power of Nutrition.
The Concept of Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA) proposes random, unguided, purposeless events causing the generation of goal-oriented mechanisms to establish a relationship, partnership, association, bonding, or cooperation between energy yielding molecules of Nonliving Matter and energy demanding molecules of Living Matter. The Concept of LUCA is associated with the hypothesis of a “Leaky” Cell Membrane which is not consistent with the twenty known functions of the Cell Membrane which I listed below the review.
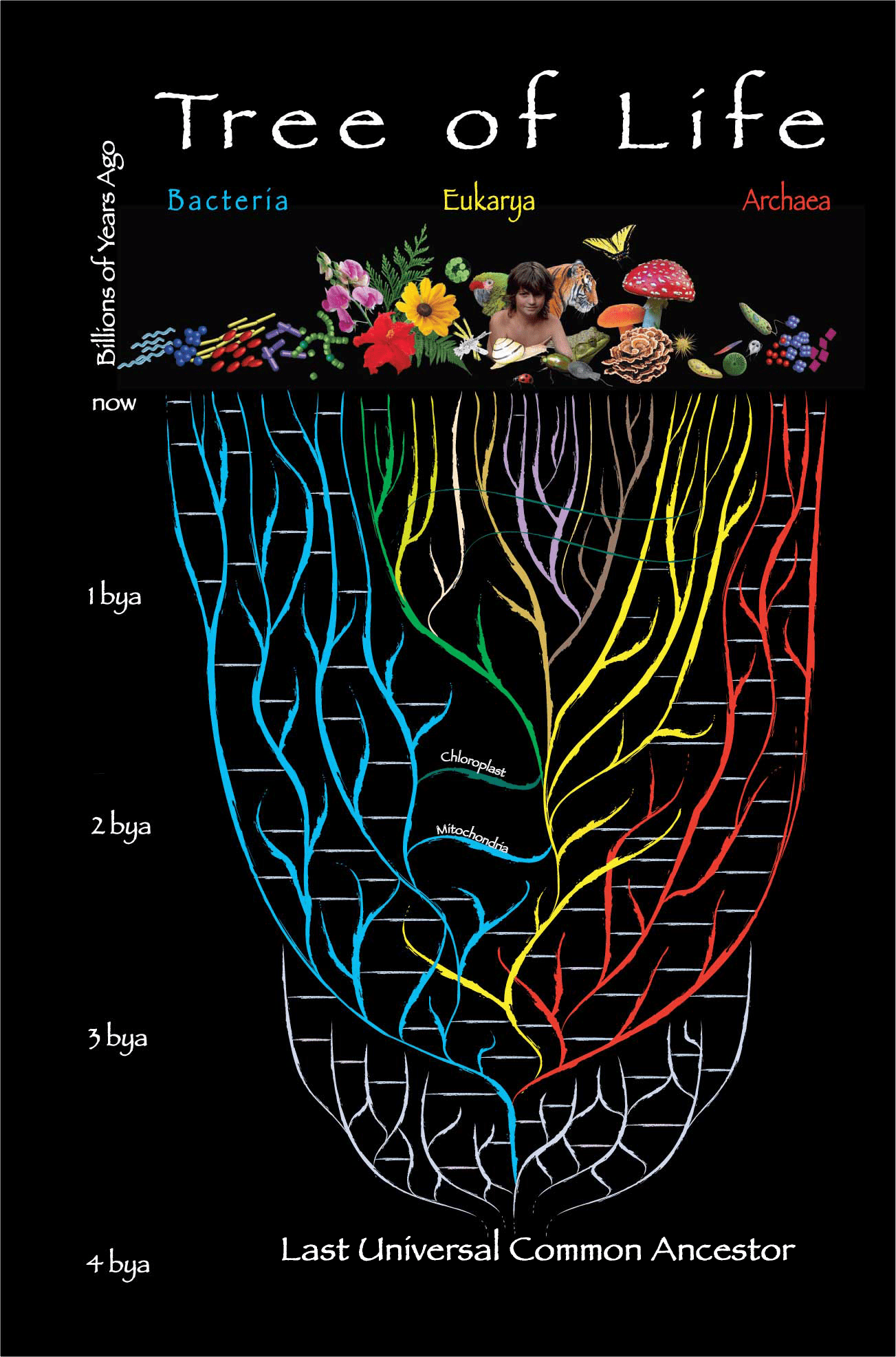
Four Billion-Year-Old Mystery of Last Universal Common Ancestor Solved

By Hannah Osborne August 12, 2014
Last common ancestor of life on Earth came from ancient oceans. DJ /Fotolia A four-billion-year-old mystery surrounding the one common ancestor of all life on Earth has been solved by scientists.
All life evolved from a single-celled organism known as life’s Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA). However, few details are known about what it looked like, how it lived and how it evolved.
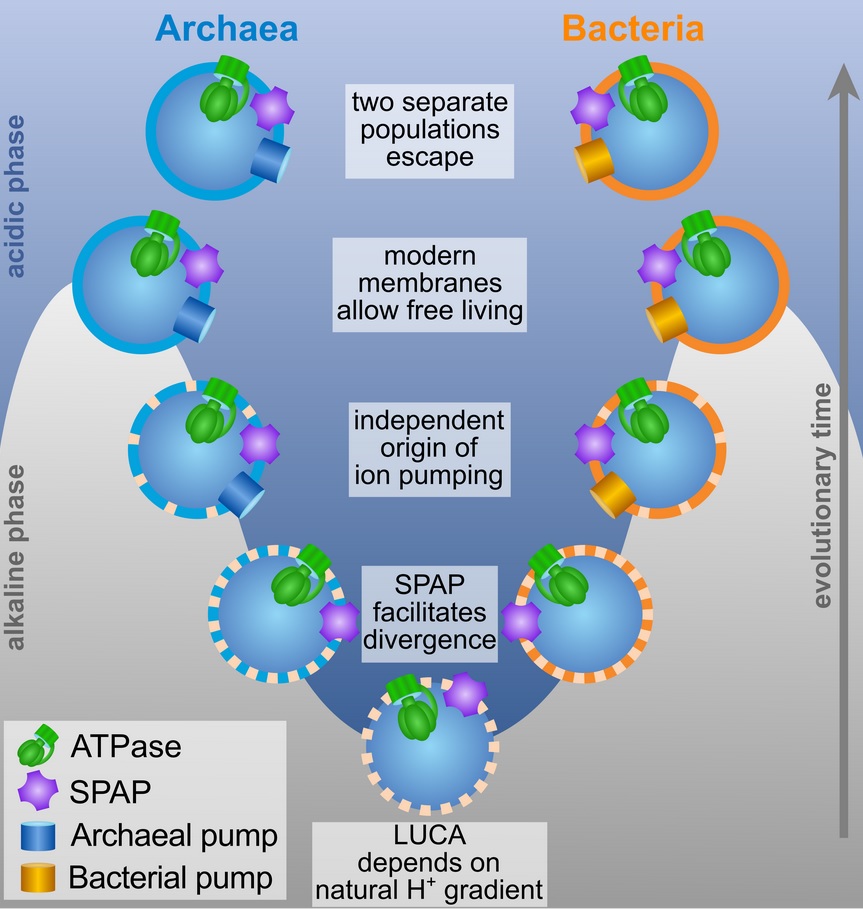
Now scientists at University College London (UCL) have discovered that LUCA had a “leaky membrane” which allow it to absorb energy from light, while still holding the other components necessary for life inside it.
Researchers discovered this by modeling how the LUCA’s membrane changed to enable its descendants to move to more challenging environments, and eventually evolve into two distinct types of single-celled organisms: bacteria and archaea.
Data suggests LUCA lived in ancient seawater where liquid dense with protons (sub-atomic particles positively charged with electricity) mixed with warm alkaline fluid from vents which had fewer protons.
The difference in concentrations allowed protons to flow into the cell, which led to the production of a molecule called ATP. This transfers energy through a cell, powering its growth.
Ion pumping (which enables cells to store energy) and phospholipid membranes (cell walls made of fat cells) evolved independently in archaea and bacteria. However, experts say this could only have happened if the membrane was ‘leaky’ – in that it allowed protons to leave the cell spontaneously, so more could enter to boost growth.
The study’s leader Nick Lane said: “In these deep-sea vents, there is a continuous flow of alkaline fluids which mix with the ocean waters. When they mix, the fluids neutralize each other, and that stops any build-up of charge which would otherwise prevent protons flowing into the cell.
“If the first cells had leaky membranes, then protons could enter and then be neutralized, or leave again, almost as if there was no barrier at all. What we’ve shown is that the rate at which protons enter and leave is high enough to power the growth of cells via proteins embedded in the membrane.
“So LUCA could have been powered by natural proton gradients in vents, but only if it had a really leaky membrane, completely unlike today’s cells.”
Victor Sojo, the first author of the study, said: “Exploiting gradients is universal across all life, but understanding how LUCA used one to drive growth gave us a bit of a chicken-and-egg problem: LUCA wouldn’t make a gradient if it didn’t know how to exploit it, but how could it learn how to exploit a gradient if it didn’t make one in the first place? We propose that natural proton gradients provide a solution because LUCA didn’t have to make the gradient; it was already there for free.”
The study was published in the journal PLoS Biology
The Inheritance of Cytoplasmic Membrane or Cell or Plasma Membrane


The Functions of Cytoplasmic Membrane or Cell Membrane or Biological Membrane:
1. Protection: It protects the cell from its surroundings or extracellular environment. Plant cell possess wall over the plasma membrane for extra protection and support.
2. Holding cell contents: Plasma membranes hold the semi fluid protoplasmic contents of the cell intact; thus keeping the individuality of the cell.
3. Selective Permeability: Cell membrane allows only selected or specific substances to enter into the cell and are impermeable to others.
- Gases like O2 and CO2 can diffuse rapidly in solution through membranes.
- Small compounds like H2O and methane can easily pass through where as sugars, amino acids and charged ions are transported with the help of transport proteins.
- The size of the molecules which can pass through the plasma membrane is 1-15 A0. This property is responsible for keeping a cell ‘as a cell’, an individual unit.
4. Shape: It maintains form and shape of the cell. It serves as site of anchorage or attachment of the cytoskeleton; thus providing shape to the cell (especially in animal cells without cell wall).
5. Organelles: Cell membrane delimits or covers all sub-cellular structures or organelles like nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, microbodies etc. thus protecting them form the surroundings and also helps in maintaining a constant internal environment.
6. Compartmentalization: Cell membrane separate the cells from their external environment and cell organelle from cytosol. It help the cells and their organelles to have their own micro environments, structural and functional individuality.
7. Cell Recognition: With the help of glycolipids and glycoproteins on its surface, cell membranes are able to differentiate similar cells from dissimilar ones, foreign substances and cells own materials. Cell recognition is useful for tissue formation and defence against microbes.
8. Antigens: Cell membranes possess antigens which determine blood grouping, immune response, acceptance or rejection of a transplant (graft rejection by MHC’s on plasma membrane).
9. Microvilli: They are microscopic finger like projections of plasma membrane present on some cells like intestinal epithelial cells, which are involved in a wide variety of functions, including increasing surface area for absorption, secretion, cellular adhesion etc.
10. Sheaths of cilia and flagella: Cilia and flagella are projections from the cell; made up of microtubules which are covered by an extension of the plasma membrane.
11. Cytoplasmic bridges in plasmodesmata and gap junctions: Plasmodesmata in plant cells and gap junctions in animal cells; meant for intercellular transport and communication, form cytoplasmic bridges between adjacent cells through plasma membrane.
12. Endocytosis and Exocytosis: Bulk intake of materials or endocytosis occurs through development of membrane vesicles or invagination and engulfing by plasma membrane.
Exocytosis: It is reverse of endocytosis that provides for releasing waste products and secretory materials ot of the cells with the help of plasma membrane.
13. Impulse transmission in neurons: The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the plasma membrane of the neuron
14. Cell metabolism: Cell membranes control cell metabolism through selective permeability and retentivity of substances in a cell.
15. Electron transport chain in bacteria: In bacteria; Electron transport chain is located in cell membrane.
15. Electron transport chain in bacteria: In bacteria; Electron transport chain is located in cell membrane.
16. Osmosis through cell membrane: It is movement of solvent molecules (generally water) from the region of less concentrated solution to the region of high concentrated solution through a semi permeable membrane. Here the semi permeable membrane that helps in osmosis is the cell membrane. Eg: Root cells take up water from the soil by osmosis
17. Carrier proteins for active transport: They occur in the cell membranes and control active transport of substances. Example, GLUT1 is a named carrier protein found in almost all animal cell membranes that transports glucose across the bilayer or plasma membrane.
18. Plasma Membrane enzymes: Many enzymes are present on the plasma membrane with wide variety of catalytic activity. Example: Red blood cell plasma membranes contain a number of enzymes such as ATPases, anion transport protein, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, protein kinases, adenylate cyclase, acetylcholinesterase.
19. Cell Membrane Receptors: Receptor on the plasma membrane performs signal transduction, converting an extracellular signal into an intra-cellular signal. Membrane possess receptors for hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies and several other biochemicals.
20. Plasma membrane assisted Cell movements: Undulation and pseudopodia are cell membrane phenomenon involved in cell movement. Amoeba, macrophages and WBCs move with the helps of temporary organelles like pseudopodia. Pseudopods are temporary cytoplasmic projections of the cell membrane in certain unicellular protists such as Amoeba. Some mammalian cells such as fibroblasts can move over a solid surface by wave like undulations of the plasma membrane.
The Ground Substance of Spiritualism and Spirituality. The vital characteristics, the animating principles of Protoplasm could be known by observing Amoeba proteus. The Living Substance works as an organ of Motion or Movement, as an organ of Nutrition, and as an organ of Reproduction to generate new cells which have a life span of their own. In these physiological functions, I describe the characteristics such as Cognition, Consciousness, Memory, and Intelligence as spiritual attributes of Life as they bring functional unity and harmony in the interactions between different parts of the same individual organism while it exists in an environment as a member of a biological community.